Open “Exchange Management Shell”
Shortcut refs to: (C:\WINDOWS\system32\windowspowershell\v1.0\powershell.exe -PSConsoleFile “C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\bin\exshell.psc1” -noexit -command “. ‘C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\bin\Exchange.ps1′”)
If this is not installed, look at the following article for installing Exchange: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb123694(EXCHG.80).aspx
Don’t get the Exchange Management Shell & Windows Powershell mixed up – for Windows Powershell see:
Adding send as permissions to mailbox:
Add-ADPermission "Mailbox" -User "Domain\User" -Extendedrights "Send As" |
Add-ADPermission "Mailbox" -User "Domain\User" -Extendedrights "Send As"
Adding full access permissions to mailbox:
Add-MailboxPermission "Mailbox" -User "Trusted User" -AccessRights FullAccess |
Add-MailboxPermission "Mailbox" -User "Trusted User" -AccessRights FullAccess
Adding full access permissions to ALL mailboxes:
Get-Mailboxdatabase | Add-AdPermission -User "Username" -AccessRights GenericAll |
Get-Mailboxdatabase | Add-AdPermission -User "Username" -AccessRights GenericAll
List all mailbox stores in size order:
Get-MailboxStatistics | Sort-Object TotalItemSize -Descending | ft DisplayName,@{label="TotalItemSize(MB)";expression={$_.TotalItemSize.Value.ToMB()}},ItemCount |
Get-MailboxStatistics | Sort-Object TotalItemSize -Descending | ft DisplayName,@{label="TotalItemSize(MB)";expression={$_.TotalItemSize.Value.ToMB()}},ItemCount
List all mailbox stores in size order (Export to CSV / on Desktop):
Get-MailboxStatistics -Database “Mailbox Database” | Select DisplayName, LastLoggedOnUserAccount, ItemCount, TotalItemSize, LastLogonTime, LastLogoffTime | Export-CSV test.csv |
Get-MailboxStatistics -Database “Mailbox Database” | Select DisplayName, LastLoggedOnUserAccount, ItemCount, TotalItemSize, LastLogonTime, LastLogoffTime | Export-CSV test.csv
List all mailbox stores in size order:
Get-MailboxStatistics -Database “Mailbox Database” | Sort -Property TotalItemsize | Format-Table DisplayName, LastLoggedOnUserAccount, ItemCount, @{expression={$_.totalitemsize.value.ToMB()};label=”Size(MB)”}, LastLogonTime, LastLogoffTime |
Get-MailboxStatistics -Database “Mailbox Database” | Sort -Property TotalItemsize | Format-Table DisplayName, LastLoggedOnUserAccount, ItemCount, @{expression={$_.totalitemsize.value.ToMB()};label=”Size(MB)”}, LastLogonTime, LastLogoffTime
Purge all disconnected mailboxes:
(Add all the disconnected mailboxes into a var by typing the below:)
$users = Get-MailboxStatistics | where-object { $_.DisconnectDate -ne $null } | Select DisplayName,MailboxGuid,Database |
$users = Get-MailboxStatistics | where-object { $_.DisconnectDate -ne $null } | Select DisplayName,MailboxGuid,Database
Purge all the disconnected mailboxes in the previously made var by typing the below:
$users | ForEach { Remove-Mailbox -Database $_.Database -StoreMailboxIdentity $_.MailboxGuid -confirm:$false } |
$users | ForEach { Remove-Mailbox -Database $_.Database -StoreMailboxIdentity $_.MailboxGuid -confirm:$false }
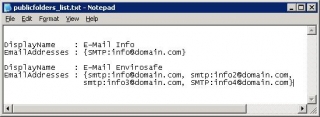
List all Public folder email addresses (output to file)
I had a request for all the email addresses associated to public mailboxes, as these are not displayed on the client in Outlook.
Method1:
Displays a list of Public Folders & Email addresses output to TXT File (FL = Formats list with full text)
Get-PublicFolder -Recurse | Get-MailPublicFolder | fl DisplayName,Emailaddresses > c:\publicfolders_list.txt |
Get-PublicFolder -Recurse | Get-MailPublicFolder | fl DisplayName,Emailaddresses > c:\publicfolders_list.txt
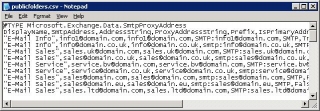
Method2: Displays a list of Public Folders & Email addresses output to CSV File:
# Export-CSV PowerShell Spreadsheet
Clear-Host
$FilePath = "c:\publicfolders.csv"
Get-MailPublicFolder | Select-Object DisplayName -expand emailaddresses| Export-CSV $FilePath |
# Export-CSV PowerShell Spreadsheet
Clear-Host
$FilePath = "c:\publicfolders.csv"
Get-MailPublicFolder | Select-Object DisplayName -expand emailaddresses| Export-CSV $FilePath
List Exchange 2007 Product Version
Get-ExchangeServer | fl name,edition,admindisplayversion |
Get-ExchangeServer | fl name,edition,admindisplayversion
List Exchange 2007 Database Size
Get-MailboxDatabase | foreach-object {add-member -inputobject $_ -membertype noteproperty -name mailboxdbsizeinGB -value ([math]::Round(([int64](get-wmiobject cim_datafile -computername $_.server -filter ('name=''' + $_.edbfilepath.pathname.replace("\","\\") + '''')).filesize / 1GB),2)) -passthru} | Sort-Object mailboxdbsizeinGB -Descending | format-table identity,mailboxdbsizeinGB |
Get-MailboxDatabase | foreach-object {add-member -inputobject $_ -membertype noteproperty -name mailboxdbsizeinGB -value ([math]::Round(([int64](get-wmiobject cim_datafile -computername $_.server -filter ('name=''' + $_.edbfilepath.pathname.replace("\","\\") + '''')).filesize / 1GB),2)) -passthru} | Sort-Object mailboxdbsizeinGB -Descending | format-table identity,mailboxdbsizeinGB
List Exchange 2007 GUID
Get-MailboxDatabase -Identity "<server name>\<storage group name>\<database name>" | Format-Table Name, GUID |
Get-MailboxDatabase -Identity "<server name>\<storage group name>\<database name>" | Format-Table Name, GUID
Public Folder Permissions via Powershell
Type the below, replacing ‘public folder name’ with your public folder name/path and you must keep the \ at the front of it and also replace ‘username’ with the username:
Add-PublicFolderClientPermission -Identity "\public folder name" -AccessRights Owner -User username |
Add-PublicFolderClientPermission -Identity "\public folder name" -AccessRights Owner -User username
Owner can be replaced with the following roles:
- None
- Owner
- PublishingEditor
- Editor
- PublishingAuthor
- Author
- Non-Editing Author
- Reviewer
- Contributor
Source: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb310789(EXCHG.80).aspx
Finding a Mailbox via Powershell
Get-Mailbox -identity findmyemail@mydomain.com |
Get-Mailbox -identity findmyemail@mydomain.com
List Members of a Distribution List (output on screen)
Get-DistributionGroupMember-identity "staff.technical" |
Get-DistributionGroupMember-identity "staff.technical"
List Members of a Distribution List including their primary email address and formatted (output to CSV on C:\)
Get-DistributionGroupMember –identity “staff.technical” | ft name, primarysmtpaddress > c:\members.csv |
Get-DistributionGroupMember –identity “staff.technical” | ft name, primarysmtpaddress > c:\members.csv
List Members of a Dynamic Distribution List
$group = Get-DynamicDistributionGroup –identity “AllStaff-DL”
Get-Recipient –RecipientPreviewFilter $group.RecipientFilter | sort name | select name > C:\dlist_members.txt |
$group = Get-DynamicDistributionGroup –identity “AllStaff-DL”
Get-Recipient –RecipientPreviewFilter $group.RecipientFilter | sort name | select name > C:\dlist_members.txt
Continue reading →