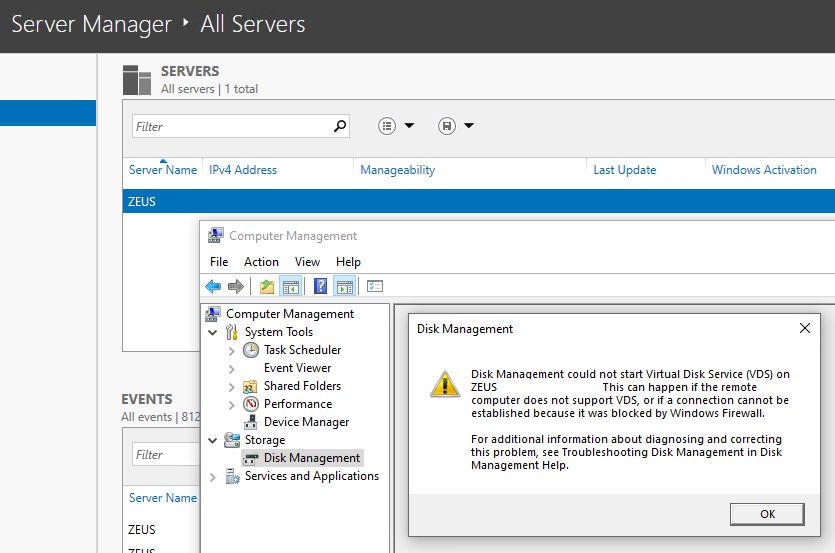
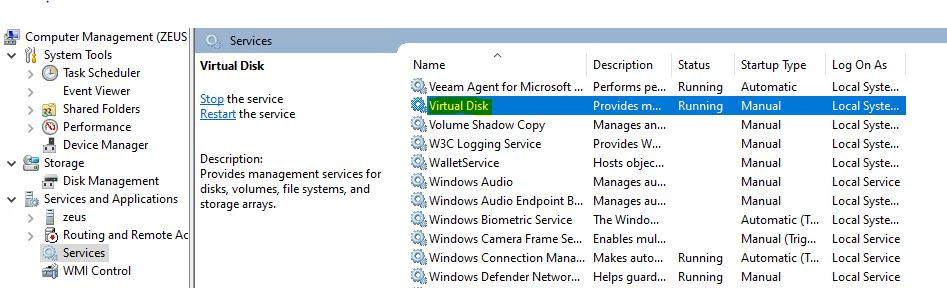
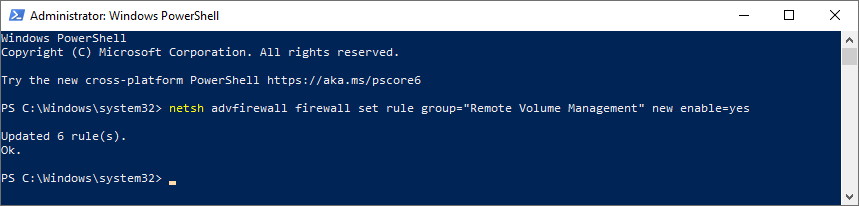
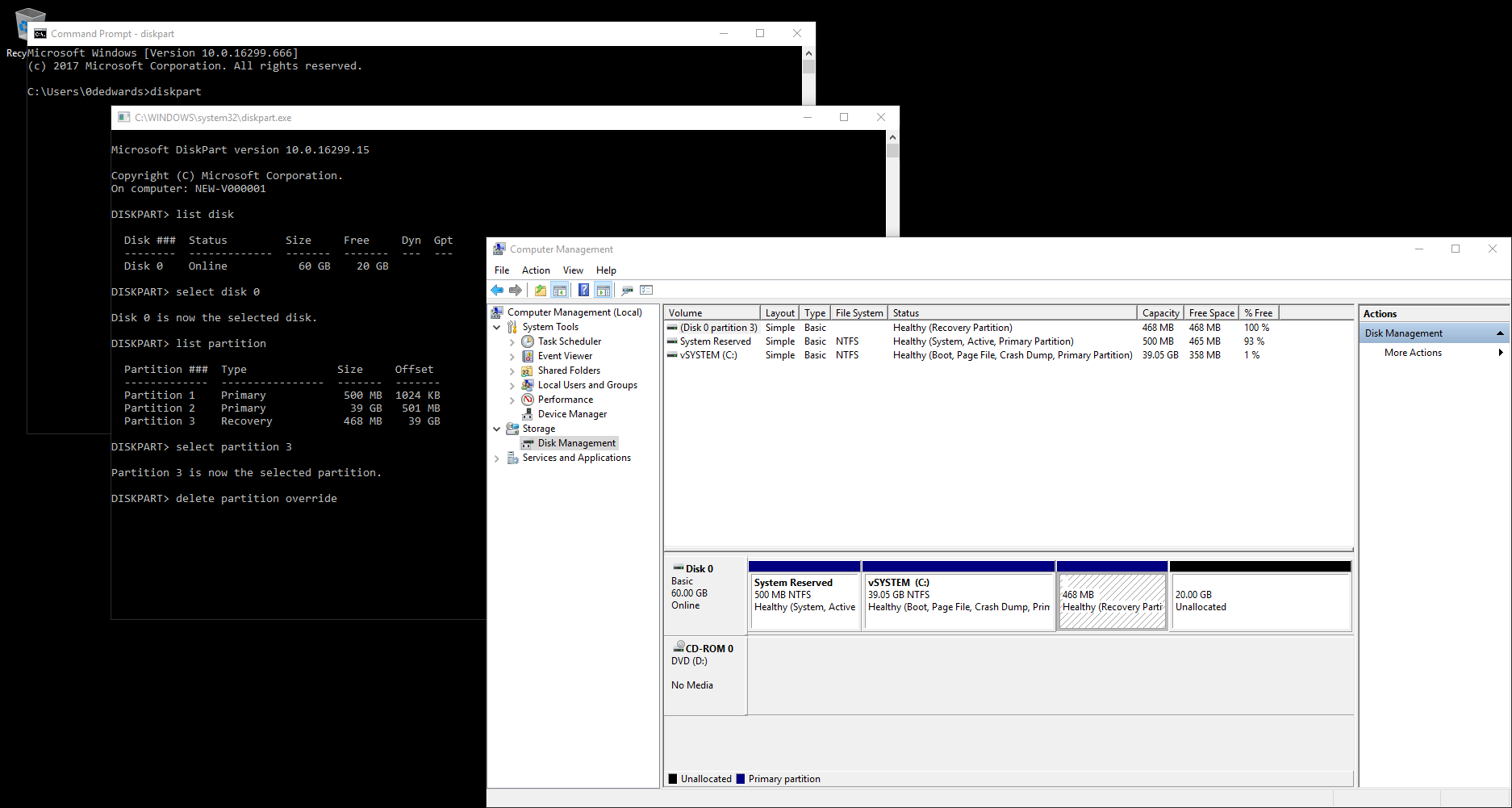
Check time service is running (Local & Remote):
sc query w32time
sc \\HOSTNAME query w32time
Displays all local time information (Local & Remote):
w32tm /query /configuration
w32tm /query /configuration /computer:HOSTNAME
Display Windows Time service status (Local & Remote):
w32tm /query /status
w32tm /query /status /computer:HOSTNAME
Display Windows Time service source (Will return one line: local CMOS vs Server) (Local & Remote):
w32tm /query /source
w32tm /query /source /computer:HOSTNAME
Display a list of peers and their status:
w32tm /query /peers
Displays current time (local source)
Time /T
Resync local computer time against time server: (run on all servers, except time server)
w32tm /resync /rediscover
Force local computer time to update against domain server (Local & Remote):
w32tm /config /syncfromflags:domhier /update
w32tm /resync /rediscover w32tm /resync
w32tm /config /syncfromflags:domhier /update /computer:HOSTNAME
w32tm /resync /rediscover w32tm /resync
Start time server via CLI (Local & Remote)
net start w32time
SC \\HOSTNAME net start w32time
Restore Windows Time Service (if it has been broken)
net stop W32Time
w32tm /unregister
w32tm /register
net start W32Time
sc query W32Time
Set Time Update NTP source
@echo off
net stop w32time
w32tm /config /syncfromflags:manual /manualpeerlist: 0.uk.pool.ntp.org
w32tm /config /reliable:yes
net start w32time
w32tm /query /peers
PAUSE
Event Viewer Error Message:
Event Type: Error
Event Source: W32Time
Event Category: None
Event ID: 12
Description: Time Provider NtpClient: This machine is configured to use the domain hierarchy to determine its time source, but it is the PDC emulator for the domain at the root of the forest, so there is no machine above it in the domain hierarchy to use as a time source. It is recommended that you either configure a reliable time service in the root domain, or manually configure the PDC to synchronize with an external time source. Otherwise, this machine will function as the authoritative time source in the domain hierarchy. If an external time source is not configured or used for this computer, you may choose to disable the NtpClient.
To resolve the eventID 12:
Reference: